
Romania is expected to see only moderate growth on the horizon. Serbia, having recorded the biggest expansion of almost 100% in the 2014-2020 period, is foreseen to plateau in the upcoming years, according to the Eastern European Construction Forecasting Association’s 2021 Winter Construction Forecast Report.
EECFA (Eastern European Construction Forecasting Association) is conducting research on the construction markets of 8 Eastern-European countries such as Bulgaria, Croatia, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovenia, Turkey and Ukraine.
The EECFA is more optimistic for 2022 in the Southeast European region than in the previous forecast round. The drop in 2023 is caused by Bulgaria; the awaited shrinkage is so sizeable there that expansion elsewhere in the region might not counterbalance it. Expansion in the East European region of EECFA is foreseen to be smaller both in 2022 and in 2023 than in the previous forecast round.
The largest Southeast European construction market of EECFA, Romania, is expected to see only moderate growth on the horizon. Serbia, having recorded the biggest expansion of almost 100% in the 2014-2020 period, is foreseen to plateau in the upcoming years.
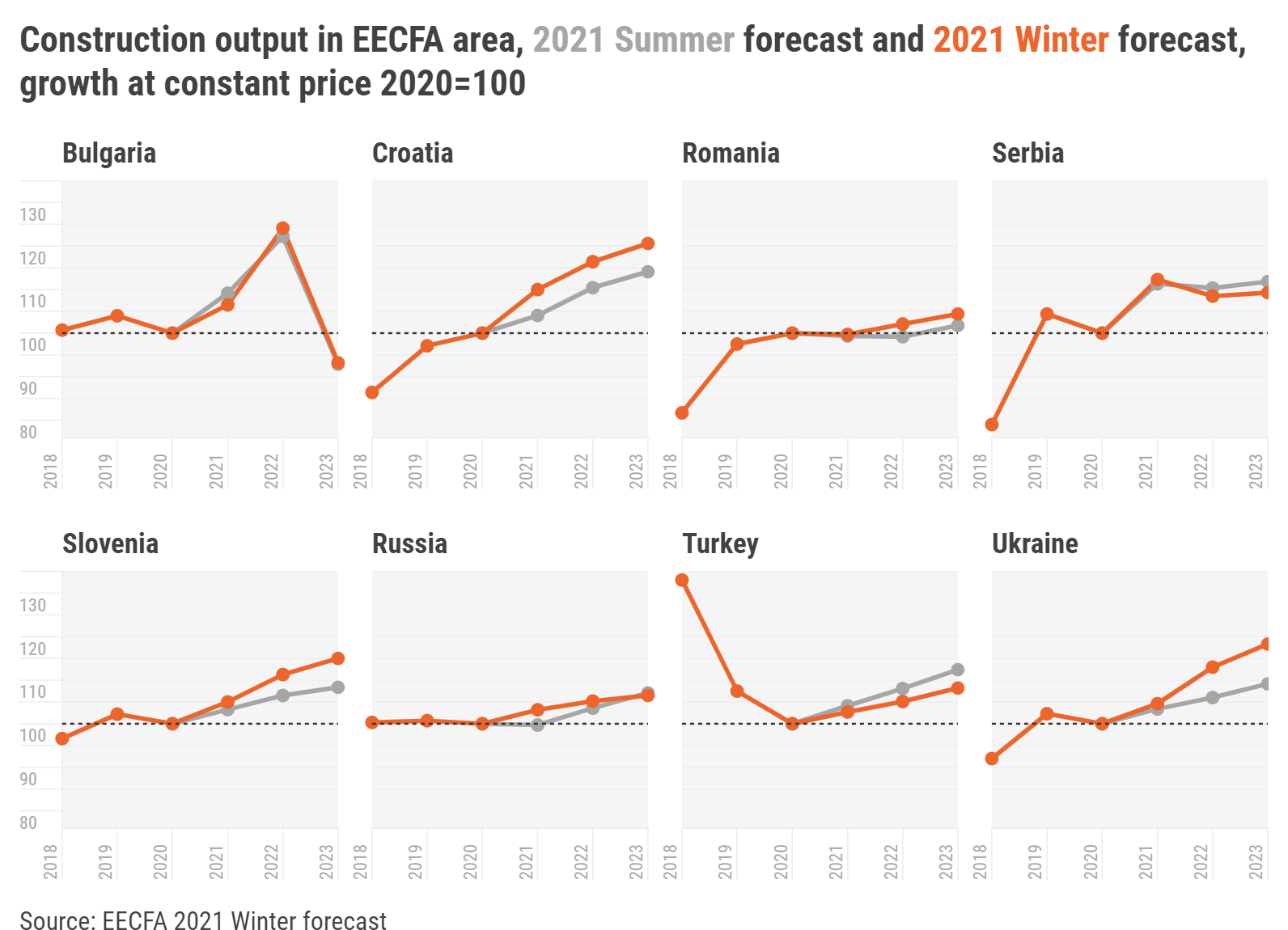
Bulgaria. The Bulgarian economy is recovering more slowly than expected, and the likely growth rate is 3.8% in 2021. However, residential construction looks strong thanks to low interest rates on housing loans, making home purchase more affordable. Real estate is also the safest and easiest way for those wanting to invest to avoid negative deposit rates. The pandemic and its lasting follow-up effects played an additionally strong cooling effect on non-residential construction because of a surge in office and industrial construction earlier and with an emptying pipeline. Zero progress on big-league infrastructure projects will take its toll on growth in civil engineering construction in 2021, but it is set to catch up in 2022. Total construction output in Bulgaria is anticipated to grow by 6.5% in 2021 and 16.5% in 2022. The lack of preparation for the new programming period 2021-2027 and the National Recovery and Resilience Plan are to negatively affect total construction output which is expected to drop by 24.9% in 2023.
Croatia. Croatia’s tourism season surpassed all expectations, driving a 16.2 percentage point swing in the country’s GDP growth, from -8.1% in 2020 to +8.1% this year, and a one-notch jump in its Fitch rating, to BBB. The near-term future of Croatia’s construction sector now depends greatly on the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly its effect on tourism. EU and international financial institution crisis-relief funding will, though, soften any blow that the disease delivers. The City of Zagreb’s budget crisis, bureaucratic delays in spending crisis-relief money and much higher construction costs are other negative factors that will affect the growth of construction output, which must be assessed not for the sector as a whole, but segment by segment (e.g., hotels vs. residential).
Romania. The economy is expected to return to pre-pandemic levels, in terms of GDP, by the end of 2021, after growing 7% in real terms. The European Commission forecasts Romania’s GDP growth rate to stay above the EU average in both 2022 (5.1%) and 2023 (5.2%), and, with the help of the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF), construction would have a positive ground to grow upon. Total construction output in 2021 is predicted to slightly decline (-0.3%), but to recover and grow in 2022 and 2023. Low interest rates and excess liquidity coalesce into an expanding residential subsector, while non-residential construction continues to be impeded by pandemic-related changes to work habits and various restrictions. On the back of the RRF and the 2014-2020 EU cohesion funds, and despite ongoing difficulties and delays in implementing projects, civil engineering construction continues to have a high potential for growth.
Serbia. After the restrictions in 2020, economic recovery came faster than expected and GDP growth is estimated to reach at least 7.3% in 2021. This strong rebound is supported by accelerated construction activity and increased capital investments, where a high single-digit expansion is projected in 2021 outputs. Construction output is fuelled by civil engineering projects, but also the robust residential and industrial related constructions. Furthermore, budgetary expenditures for investments are planned to reach record levels, with 7.5% of GDP dedicated for this purpose in 2022. All indicators are pointing towards more extensive growth and sustained construction activity at record levels in this forecast horizon.
Slovenia. The Slovenian economy has rebounded stronger than expected after the pandemic. One of the strongest economic growth accelerators was gross fixed capital investment, causing construction output to get back on feet. Total construction output is projected to exceed EUR 4bln sooner than previously predicted – already in 2022 – and reach EUR 4,3bln in 2023. Construction cost growth will probably slow down from a hike in 2021, resulting in a more stable construction environment without supply shocks. This will enable several big civil engineering projects to continue apace, but the main contributor to construction output will be new residential projects. Of course, our forecasts remain contingent on the condition that no further lockdowns hinder the overall economic activity.



